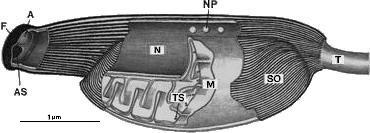
The spermatozoon of Ciona intestinalis has architectural features that are characteristic of ascidian spermatozoa.
It has an elongated head (approximately 4 um long) with a wedge-shaped tip and a mitochondrion (M) which is closely applied laterally to the nucleus (N).
An acrosome (A) is present at the anterior region of the head, which appears as a flattend vesicle (about 150nm x 160nm x 60nm).
At the anterior-most tip of the head, apical substance (AS) which is an accumulation of granular material, approximately 5-7 nm in diameter, is recognized.
Fuzzy materials (surface ornamentation) decorate the external surface of the plasmalemma enclosing the head.
Nuclear pores (NP) are present.They appear sometimes in the anterior region of the head.
Tubular structures (TS), approximately 20 nm in diameter, are present in the mitochondrion just inside the inner membrane running antero-posteriorly.
F, fuzzy materials; SO, surface ornamentation; T; tail.
Review article for details: Zoological Science 7, 989-998 (1990)